On November 1, 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved VOQUEZNA® (vonoprazan) as a new treatment for the healing and maintenance of erosive esophagitis and the relief of heartburn associated with erosive esophagitis in adults. This FDA approval marks the first innovation in erosive esophagitis management in nearly 30 years.
Erosive Esophagitis Epidemiology
In the United States, there are over 65 million patients living with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Of these patients, approximately 30% experience erosive esophagitis. Erosive esophagitis occurs when acidic stomach contents reflux into the esophagus and erode the mucosa. If not adequately treated, the bothersome heartburn-like symptoms associated with erosive GERD can progress to more serious conditions, such as Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal cancer.
Mechanism of Action
Vonoprazan is a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker (PCAB) that suppresses basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion from the gastric parietal cells via inhibition of the H+, K+-ATPase system, essentially functioning as an improved type of proton pump inhibitor.
Clinical Trial Data
In the large phase III randomized, double-blind, parallel-group PHALCON-EE trial, vonoprazan was compared to lansoprazole and found to be noninferior and superior for the healing and maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis, especially in patients with more severe esophagitis.
Participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive either once-daily vonoprazan 20 mg or lansoprazole 30 mg for 8 weeks. The authors found that 92.9% of participants in the vonoprazan group achieved healing by week 8 compared to 84.6% of participants in the lansoprazole group (difference, 8.3%; 95% CI, 4.5-12.2%; P < 0.0001).
In the maintenance phase, participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive once-daily vonoprazan 20 mg, vonoprazan 10 mg, or lansoprazole 15 mg for 24 weeks. It was found that 80.7% of participants in the vonoprazan 20 mg, 79.2% in the vonoprazan 10 mg, and 72.0% in the lansoprazole groups maintained healing after 24 weeks (P < 0.0001 for both comparisons).
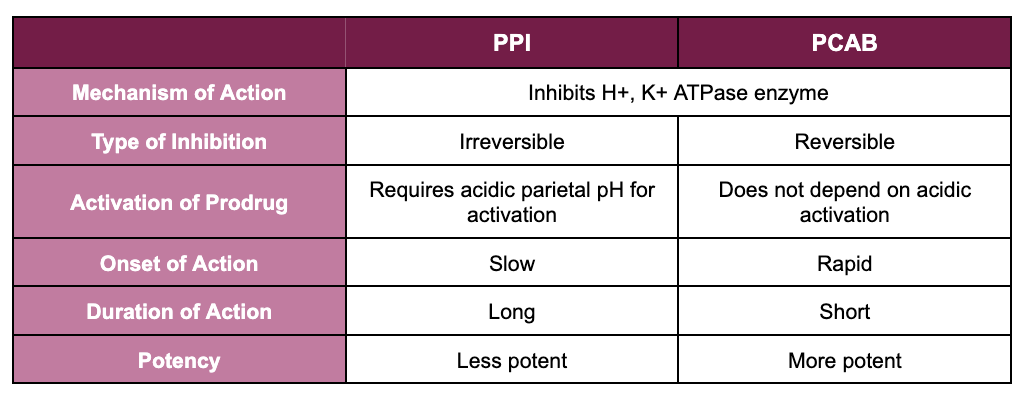
The table below outlines some of the pharmacological differences between PPIs and PCABs.
Dosage and Dosage Adjustments
Vonoprazan is manufactured as two different-strength oral tablets: 10 mg and 20 mg. The medication is dosed differently depending on the indication, as shown in the table below.
| Healing of Erosive Gastritis and Relief of Heartburn | |
| 20 mg once daily for 8 weeks | |
| Maintenance of Healed Erosive Esophagitis and Relief of Heartburn | |
| 10 mg once daily for up to 6 months |
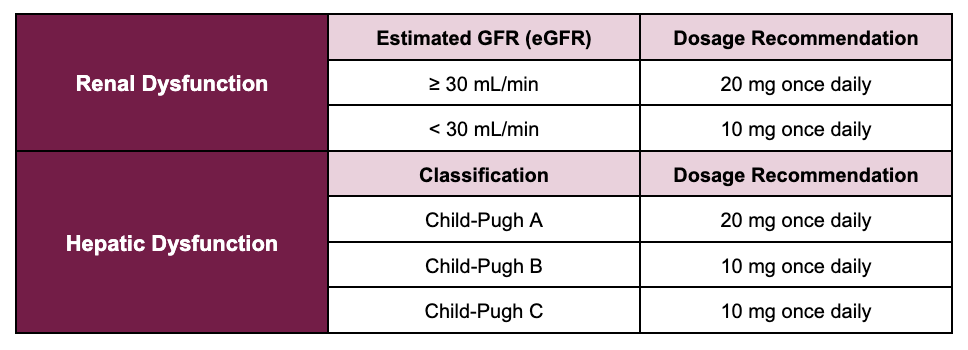
For these two indications, the renal and hepatic dosage adjustments are the same and outlined in the following table.
Adverse Effects, Precautions, and Contraindications
In patients treated with vonoprazan, the most common adverse effects are GI-related and include gastritis, dyspepsia, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and abdominal distension. With longer-term use, as in the setting of maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis, patients may also experience hypertension and urinary tract infections.
Because of vonoprazan’s PPI-like mechanism of action, this agent shares many of the same precautions, such as gastric malignancy, Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea, bone fractures, vitamin B12 deficiency, hypomagnesemia and mineral metabolism, fundic gland polyps, and interactions with investigations for neuroendocrine tumors. Additional vonoprazan-specific precautions include acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and severe cutaneous adverse reactions.
Contraindications include known hypersensitivity to vonoprazan and concomitant use of rilpivirine-containing products, which will be addressed in the following section.
Vonoprazan Drug Interactions
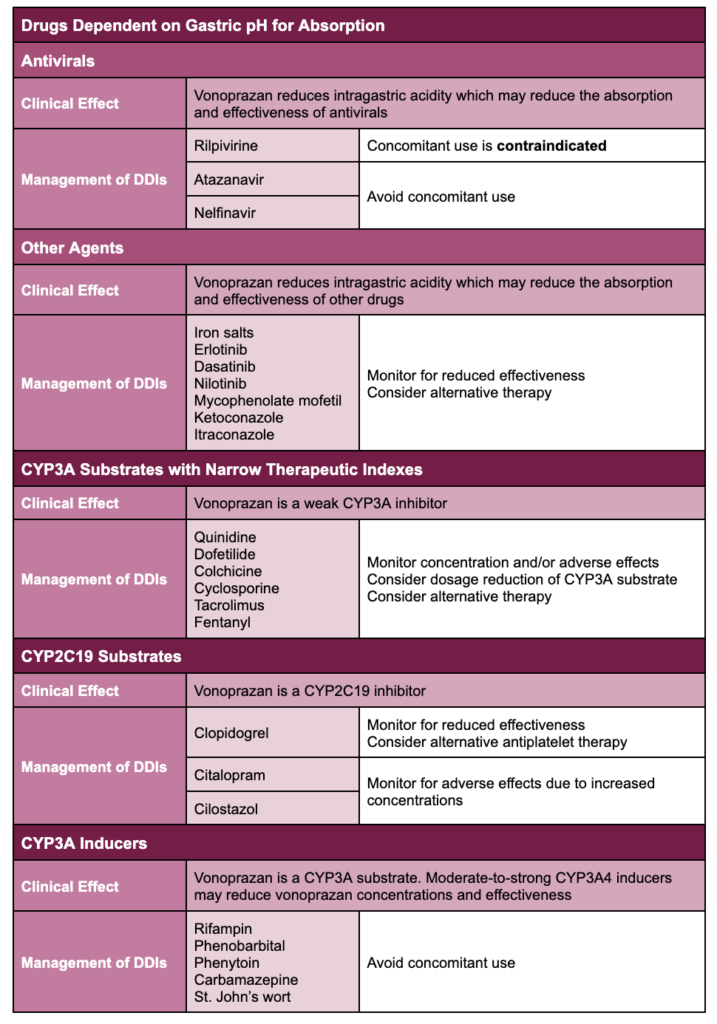
The following table outlines clinically meaningful drug interactions identified during clinical trials as well as predicted drug interactions based on vonoprazan’s pharmacology.
Conclusion
Vonoprazan is a novel once-daily acid-suppressing medication newly approved by the FDA for the healing and maintenance of erosive esophagitis and the relief of heartburn associated with erosive esophagitis in adult patients. Clinical trial data suggests that vonoprazan is superior to PPI therapy for these indications and may be a revolutionary treatment for patients with severe erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease.
The article was written by Kaitlyn Nichols in collaboration with Eric Christianson, PharmD, BCPS, BCGP
- 30 medication mistakes PDF
- 18+ Page Drug Interaction PDF
- 10 Commandments of Polypharmacy Webinar based on my experiences in clinical practice
Popular Amazon Books
References:
- Laine L, DeVault K, Katz P, et al. Vonoprazan Versus Lansoprazole for Healing and Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis: A Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology. 2023;164(1):61-71.
- Phathom Pharmaceuticals Announces FDA Approval of VOQUEZNA® (vonoprazan) Tablets for the Treatment of Erosive GERD and Relief of Heartburn Associated with Erosive GERD in Adults | Phathom Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Phathom Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Published 2023. https://investors.phathompharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/phathom-pharmaceuticals-announces-fda-approval-voqueznar (Accessed: May 1, 2024).
- Rawla P, Sunkara T, Ofosu A, Gaduputi V. Potassium-competitive acid blockers – are they the next generation of proton pump inhibitors?. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2018;9(7):63-68.
- Vonoprazan, IBM Micromedex® DrugPoint Summary (electronic version). IBM Watson Health, Greenwood Village, Colorado, USA. Available at: https://www-micromedexsolutions-com.ezp3.lib.umn.edu (Accessed: May 1, 2024).
- VOQUEZNA® (vonoprazan) [package insert]. Buffalo Grove, IL: Phathom Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2023.








0 Comments