Beta-blockers are a class of medication that is frequently used for cardiac and cardiovascular purposes. Selectivity and evidence of benefit often guide selection, but one thing that may get overlooked is beta-blocker interactions in relation to CYP enzymes. Not all beta-blockers interact with CYP enzymes and those that don’t always follow a pattern.
We wanted to create this table of beta-blocker interactions and CYP enzymes to demonstrate which medications in this class may be affected by commonly used medications that can inhibit or induce certain CYP450 enzymes and how they may impact each individual beta-blocker. These are definitely differences that may show up on a pharmacist board exam!
| Drug Name | Metabolism and Elimination | CYP Drug Interactions | Results of Interaction |
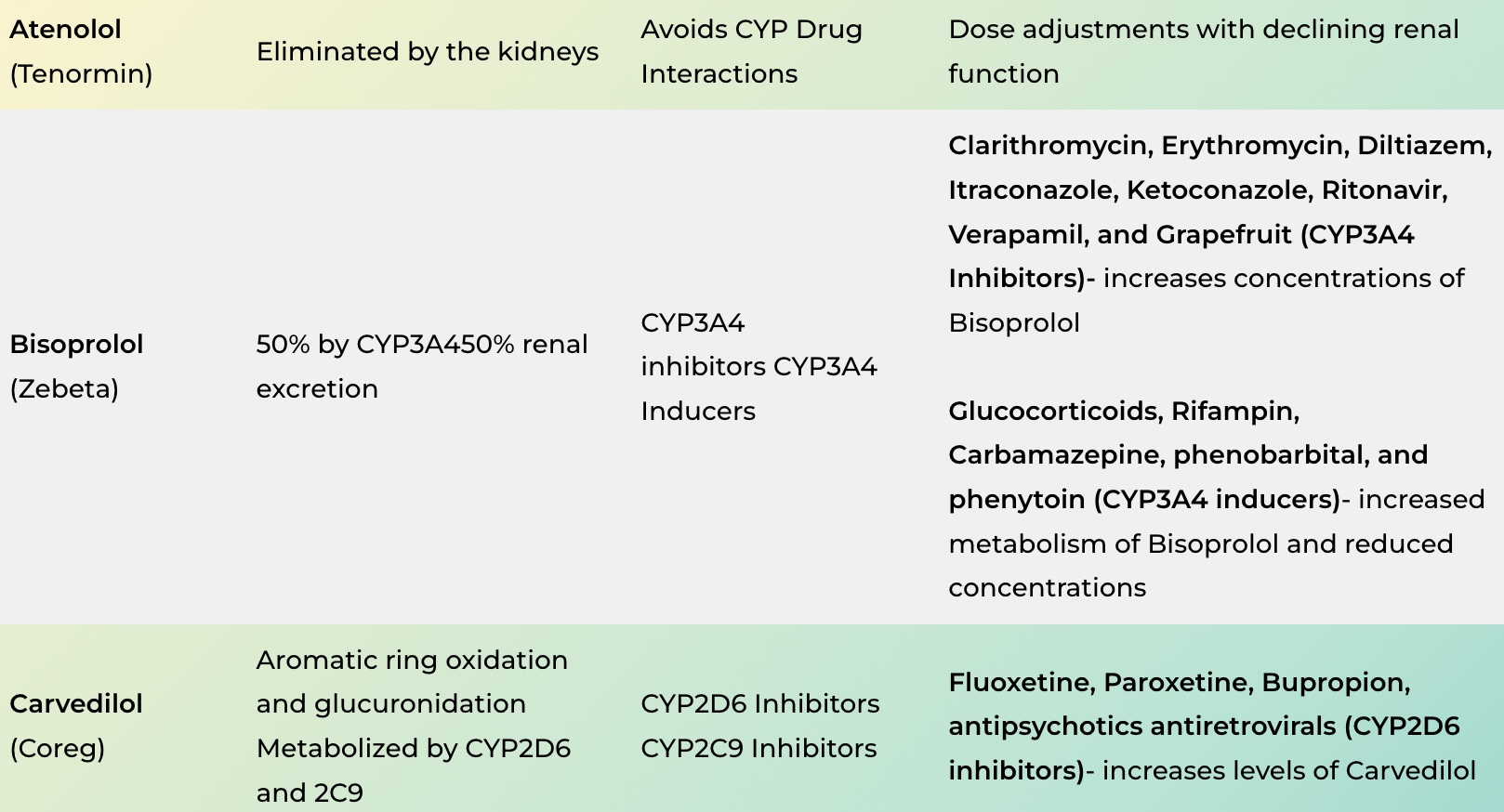
| Atenolol (Tenormin) | Eliminated by the kidneys | Avoids CYP Drug Interactions | Dose adjustments with declining renal function |
| Bisoprolol (Zebeta) | 50% by CYP3A450% renal excretion | CYP3A4 inhibitors CYP3A4 Inducers | Clarithromycin, Erythromycin, Diltiazem, Itraconazole, Ketoconazole, Ritonavir, Verapamil, and Grapefruit (CYP3A4 Inhibitors)- increases concentrations of Bisoprolol Glucocorticoids, Rifampin, Carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin (CYP3A4 inducers)– increased metabolism of Bisoprolol and reduced concentrations |
| Carvedilol (Coreg) | Aromatic ring oxidation and glucuronidation Metabolized by CYP2D6 and 2C9 | CYP2D6 Inhibitors CYP2C9 Inhibitors | Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Bupropion, antipsychotics antiretrovirals (CYP2D6 inhibitors)– increases levels of Carvedilol |
| Esmolol (Brevibloc) | Metabolized by esterases in red blood cells | Avoids CYP Drug Interactions | N/A |
| Labetalol (Normodyne, Trandate) | Metabolized by UGT2B7 and UGT1A1 | Avoids CYP Drug interactions | N/A |
| Metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL) | Metabolized by CYP2D6 | CYP2D6 inhibitors | Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Bupropion, sertraline, antipsychotics antiretroviral (CYP2D6 inhibitors)-increases concentrations of Metoprolol |
| Nadolol (Corgard) | Eliminated by the kidneys | Avoids CYP Dose Interactions | Dose adjustments with declining renal impairment |
| Nebivolol (Bystolic) | Metabolized by CYP2D6 and glucuronidation | CYP2D6 inhibitors | Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Bupropion, antipsychotics antiretrovirals – increases concentrations of Nebivolol |
| Pindolol (Visken) | Undergoes glucuronidation or sulfate conjugation. | Avoids CYP drug interactions. | N/A |
| Propranolol (Inderan) | Aromatic ring oxidation and glucuronidation CYP2D6, 1A2, 2C19 involvement | CYP2D6 inhibitors CYP1A2 inhibitors CYP2C19 inhibitors | Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Bupropion, antipsychotics antiretrovirals – increases levels of propranolol Cimetidine, Ciprofloxacin, Fluvoxamine, Isoniazid, Ritonavir (CYP1A2 inhibitors)- increases levels of propranolol Fluconazole, Cimetidine, Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, Tenioposide (CYP2C19 inhibitors)- increases levels of propranolol |
| Sotalol (Betapace) | Primarily eliminated by the kidneys | Avoids CYP drug interactions | Dose adjustments with declining renal impairment |
| Timolol (Blocadren) | Metabolized by CYP2D6 and little involvement with 2C19 | CYP2D6 inhibitors | Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Bupropion, antipsychotics antiretroviral (CYP2D6 inhibitors)- increases concentration of Timolol |
Bisoprolol has a compelling indication for heart failure and in my experience is seldom used compared to carvedilol and metoprolol (podcast). It can significantly interact with medications that affect CYP3A4.
CYP2D6 is a critical enzyme for many of the most commonly used beta-blockers. Metoprolol and carvedilol are the two frequently used agents that may be impacted by our patients taking a CYP2D6 inhibitor or inducer.
Propranolol is probably the most complicated beta-blocker when it comes to CYP drug interactions. This medication is broken down by three CYP enzymes. While this does make it more complex, it can also blunt the overall effect of the interaction if there are other pathways for breakdown. I think it is important to emphasize close monitoring when new drugs are started with propranolol because there is a significant potential for many drugs to interact with it.
Note that we have a few beta-blockers that are primarily eliminated via the kidney. Atenolol, sotalol, and nadolol avoid CYP enzymes altogether. A few others are metabolized by non-CYP mechanisms. Esmolol, labetalol, and pindolol are metabolized by alternative methods as you can see in the beta-blocker CYP enzyme table above.
Looking for more on beta-blocker drug interactions? In this previous post, I discuss some options to address the beta-blocker albuterol interaction.


This is super-helpful; a great reminder for closer prescription audits for those with compelling indications as Cardiovascular diseases. Thanks