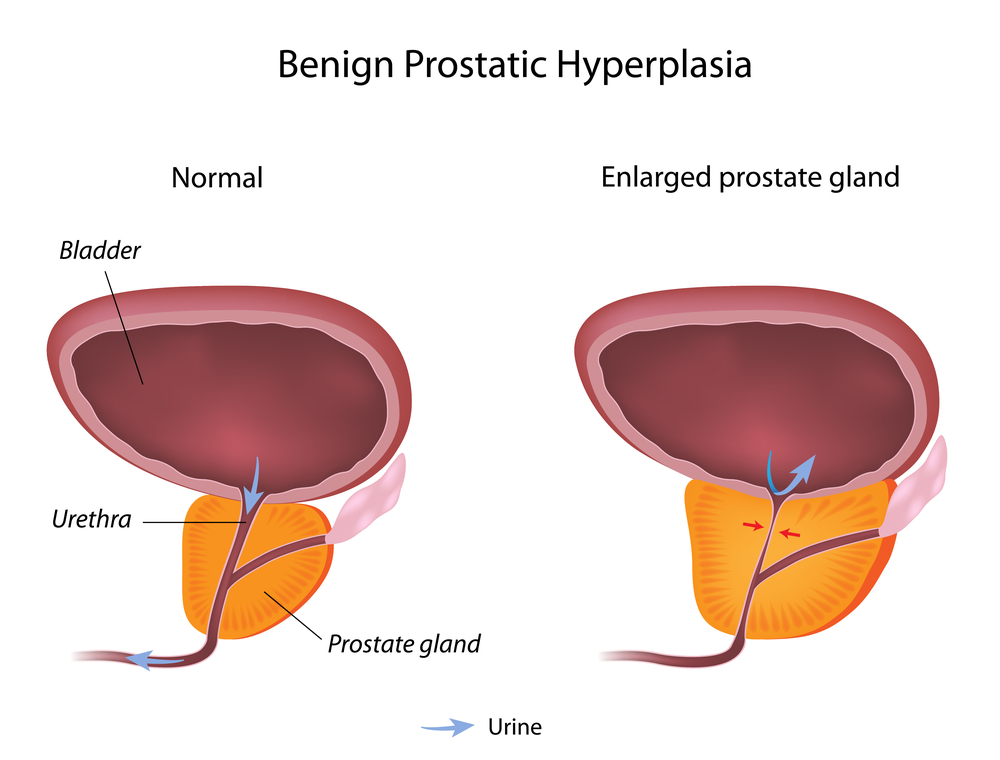
85 year old male with a recent operation for a knee replacement was discharged on hydrocodone/APAP 5/325 1-2 every four hours as needed as well as Vistaril (hydroxyzine) 25-50 mg every six hours as needed for pain management. Within a couple days of significant prn use for the pain, the patient was understandably dealing with some constipation issues that were easily managed with Senna-S 2 tablets daily. After about 5-7 days, this patient began to have worsening urinary retention and was placed on Flomax (tamsulosin) 0.4 mg daily to help treat the retention. The following day, the retention was getting even worse and a Foley catheter had to be placed. This gentleman did have a history of BPH and retention, and here’s a perfect demonstration why anticholinergics (Vistaril) in the elderly should be avoided or at least be minimized. This patient was using the 50 mg dose as often as he could which was certainly worsening the urinary retention. Remember, can’t spit, see, PEE, or poop – are a few of the anticholinergic effects that can be pretty nasty in the elderly!
Anticholinergics can Worsen BPH
7 Comments
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- 6 Notorious Side Effects of Anticholinergics and How They Contribute to the Prescribing Cascade - Med Ed 101 - […] retention – Here’s a classic case of the prescribing cascade involving anticholinergics causing urinary […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.
Written By Eric Christianson


Nice reminder, classic patient. Thanks.
Thanks Mike!
It’s for itch related to use of narcotics if one is allergic or sensitve . Highly sedating and can increase risk of falls in seniors as well.
Sorry, but I’ve never seen Vistaril being prescribed for pain. Why?
In this case hydroxyzine was being used to potentiate the analgesia of the opoid but by doing so some side effects were just elleviated .Too old school
SLUD was the acronym we used in the old days to help memorize the common side effects of cholinergics. It stands for Salivation, Lacrimation, Urination and Defecation, respectrively. One would expect the opposite effects from use of anticholiergics. Just a thought.
Great example – complete medical history is vital